True Market Price New Car Buying Guide
Defining “True Market Price”
True market price new car – Understanding the true market price of a new car goes beyond the sticker price. Several factors influence the final price a buyer pays, creating a complex interplay between manufacturer recommendations, dealer practices, and market dynamics.
Factors Influencing New Car Prices Beyond MSRP
The Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP) is just a starting point. Other factors significantly impact the final price. These include dealer markups, regional demand, vehicle options and packages, financing incentives, and prevailing economic conditions. A car’s popularity, its features, and even the time of year can all influence its market price.
MSRP, Invoice Price, and Dealer’s Cost
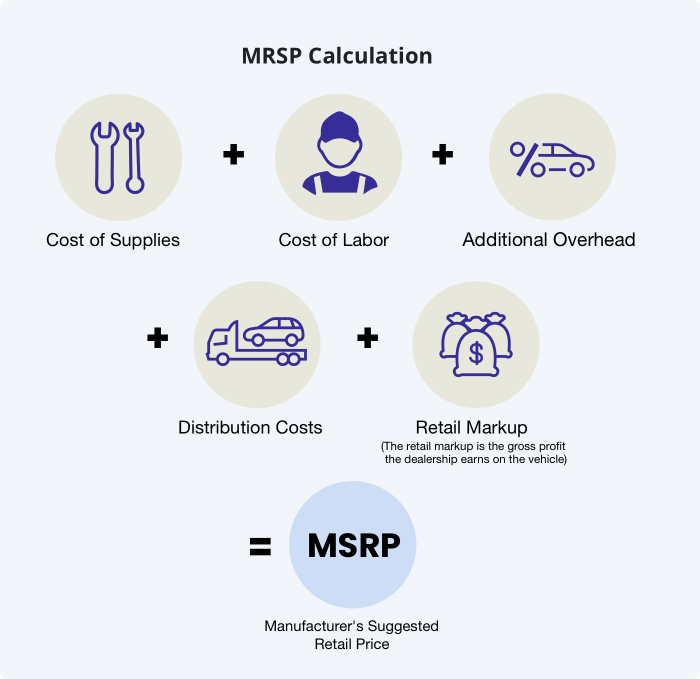
The MSRP is the price the manufacturer suggests retailers should sell the vehicle for. The invoice price is what the dealership pays the manufacturer. The dealer’s cost includes additional fees and transportation charges. The difference between these prices represents the dealer’s profit margin, which is subject to negotiation.
Market Conditions Impacting New Car Prices
Source: website-files.com
Several market conditions dramatically affect a new car’s price. High demand coupled with limited supply, as seen during periods of microchip shortages, leads to increased prices and longer wait times. Conversely, during economic downturns or when a specific model experiences a decline in popularity, prices tend to decrease. Seasonal changes and the introduction of new models also influence pricing.
Comparative Pricing Structures
| Car Model | MSRP | Invoice Price | Estimated Market Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Camry | $26,000 | $24,000 | $25,000 – $27,000 |
| Honda Civic | $23,000 | $21,000 | $22,000 – $24,000 |
| Ford F-150 | $35,000 | $32,000 | $33,000 – $37,000 |
Note: These are example prices and may vary based on trim level, options, and location.
Impact of Supply and Demand
The principles of supply and demand heavily influence the true market price of new cars. Limited production, high demand for specific models, and desirable features all contribute to price fluctuations.
Limited Production Runs and Market Price
When a manufacturer produces a limited number of a particular model or trim level, scarcity drives up the price. Collectors’ editions or special anniversary models often command significantly higher prices than standard versions due to their limited availability.
Determining a true market price for a new car involves considering various factors, including dealer markups and regional variations. To illustrate, understanding the pricing structure for a specific brand is crucial; you can check out the current offerings at suzuki new car price for a clearer picture. This helps contextualize how individual models fit within the broader market and contribute to the overall understanding of true market value.
Popular Car Models and Features
Popular car models and in-demand features, such as advanced safety technology, all-wheel drive, or specific engine options, increase market value. Dealers may leverage the popularity of certain features to justify higher prices.
Price Fluctuations: High-Demand vs. Low-Demand Vehicles
High-demand vehicles often sell above MSRP, sometimes with significant markups. Conversely, low-demand vehicles might sell below MSRP to incentivize sales. The difference can be substantial, illustrating the direct relationship between supply, demand, and pricing.
Supply, Demand, and Market Price Graph
A graph illustrating this relationship would have “Supply” on the x-axis and “Price” on the y-axis. The demand curve would slope downward, indicating that as price increases, demand decreases. The intersection of the supply and demand curves determines the equilibrium market price. A shift in either supply or demand will cause a corresponding change in the equilibrium price.
For instance, a decrease in supply (e.g., due to a chip shortage) would shift the supply curve to the left, leading to a higher equilibrium price.
Role of Dealers and Negotiations
Car dealerships play a crucial role in determining the final price a consumer pays. Their strategies and the buyer’s negotiation skills significantly influence the outcome.
Dealer Strategies to Influence Price
Dealerships employ various strategies, including adding dealer markups, bundling optional features, and highlighting financing incentives to influence the price. They might also use high-pressure sales tactics or emphasize the limited availability of certain models to encourage quick purchases at a higher price.
Buyer Negotiation Tactics
Effective negotiation involves researching the market price, understanding the dealer’s cost, and presenting a well-informed offer. Buyers can leverage competing offers from other dealerships, highlight negative reviews of the dealership, or focus on the out-the-door price rather than monthly payments.
Price Differences Through Negotiation
The price difference achieved through negotiation can vary widely depending on the buyer’s skills, the dealer’s willingness to negotiate, and the market conditions. In high-demand markets, negotiation might yield less significant savings, while in low-demand markets, buyers may achieve more substantial discounts.
Factors to Consider Before Negotiating
- Research the market value of the car.
- Determine your maximum budget.
- Understand financing options.
- Be prepared to walk away.
- Know the dealer’s cost (approximately).
External Factors Affecting Price
Broader economic and environmental factors significantly influence new car prices. These external forces interact with supply and demand to shape the market.
Economic Conditions and New Car Prices
Inflation directly impacts the cost of manufacturing and materials, leading to higher prices. Increased interest rates make financing more expensive, potentially affecting consumer demand and pricing. Recessions can decrease demand, resulting in lower prices and potential sales incentives.
Government Regulations and Incentives
Government regulations, such as fuel efficiency standards (like CAFE standards in the US), influence the design and manufacturing costs of vehicles, ultimately impacting their price. Government incentives, such as tax credits for electric vehicles, can make certain models more affordable, affecting their market position.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Concerns
Growing environmental concerns and stricter emission regulations push manufacturers to develop more fuel-efficient vehicles. The technology required for increased fuel efficiency can add to the manufacturing cost, influencing the final price. The demand for electric vehicles, driven by environmental concerns, also influences pricing.
Technological Advancements and Market Price
Technological advancements, such as the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving features, significantly impact market prices. The initial cost of developing and implementing these technologies is high, resulting in higher prices for vehicles incorporating them. However, as the technology matures and becomes more mainstream, prices typically decrease.
Online Resources and Price Transparency
The internet has significantly increased price transparency in the automotive market. Online tools and resources empower consumers to make informed decisions.
Online Car Pricing Tools and Market Price Transparency, True market price new car
Websites and apps that provide pricing information, such as Kelley Blue Book (KBB), Edmunds, and TrueCar, increase transparency by providing consumers with estimates of fair market prices. This empowers buyers to negotiate more effectively.
Accuracy and Reliability of Online Pricing Resources

Source: competera.net
The accuracy of online pricing resources varies. While they offer valuable estimates, it’s essential to remember that these are estimates and can differ based on location, vehicle options, and current market conditions. It’s best to use multiple resources for a more comprehensive picture.
Online Marketplaces and the Negotiation Process
Online marketplaces, such as those offered by some dealerships or third-party platforms, can streamline the car-buying process and potentially affect the negotiation process. The transparency of pricing on these platforms can influence the final price, potentially reducing the need for extensive negotiations.
Reputable Online Resources for Checking New Car Prices
- Kelley Blue Book (KBB): Strengths – Comprehensive data, detailed reports; Weaknesses – May not always reflect real-time market fluctuations.
- Edmunds: Strengths – In-depth reviews, pricing tools; Weaknesses – Can be overwhelming with information.
- TrueCar: Strengths – Connects buyers with dealers, price transparency; Weaknesses – May not be available in all areas.
- Cars.com: Strengths – Large inventory listings, user reviews; Weaknesses – Can be difficult to filter results effectively.
Key Questions Answered: True Market Price New Car
What is the best time of year to buy a new car?
Generally, the end of the month and the end of the quarter (March, June, September, December) are considered ideal times to buy, as dealerships often aim to meet sales quotas.
How much should I put down on a new car?
The ideal down payment depends on your financial situation and loan terms, but a larger down payment generally leads to lower monthly payments and less interest paid over the life of the loan.
Can I negotiate the interest rate on my car loan?
Yes, it’s advisable to shop around for the best interest rates from different lenders before finalizing your car purchase. Your credit score significantly impacts the interest rate you’ll receive.
What are common hidden fees associated with new car purchases?
Be aware of potential add-on fees such as dealer prep fees, documentation fees, and extended warranties. Carefully review all charges before signing any paperwork.




















