What is Invoice Price on a New Car Mean?
Understanding Invoice Price on a New Car: What Is Invoice Price On A New Car Mean
Source: simpleinvoice17.net
What is invoice price on a new car mean – The invoice price of a new car represents the price a dealership pays the manufacturer for the vehicle. Understanding this price is crucial for negotiating a fair deal when purchasing a new car. This article will break down the components of the invoice price, its relationship to the sticker price, and how it can be leveraged during negotiations.
Defining Invoice Price
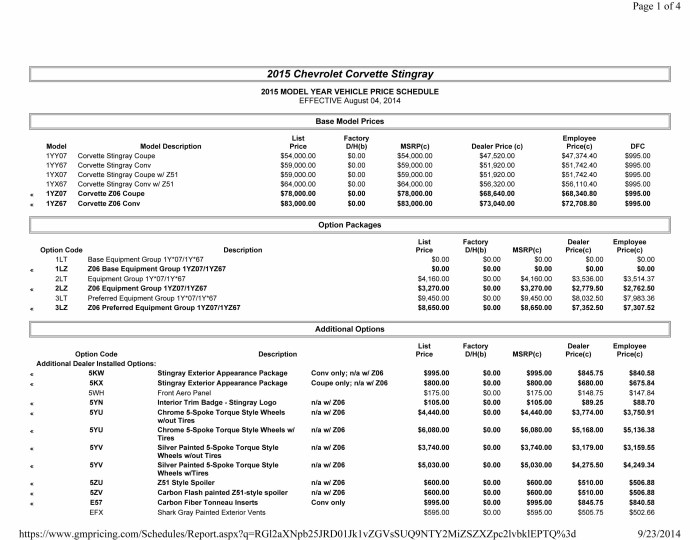
The invoice price is the net price a dealership pays the manufacturer for a vehicle. It doesn’t include the dealer’s profit margin or additional fees. Several components contribute to the invoice price, including the base vehicle price, options and packages, and destination charges (the cost of shipping the car to the dealership). The invoice price is significantly lower than the sticker price (Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price or MSRP), which is the price advertised to consumers.
The difference between the invoice price and the MSRP represents the potential profit margin for the dealership.
Factors influencing the invoice price include the vehicle’s model and trim level, popular options, manufacturer incentives, and the current market demand. A high-demand vehicle might have a higher invoice price than a less popular model, even if the MSRP is similar.
Understanding the invoice price—the price the dealership pays the manufacturer—is crucial when buying a new car. This figure serves as a valuable benchmark, helping you determine a fair price. For further guidance on achieving the best deal, check out these tips on negotiating a new car price , which can significantly impact your final cost. Ultimately, knowing the invoice price empowers you to negotiate effectively and secure a better deal.
| Vehicle Type | Manufacturer | Invoice Price | MSRP | Dealer Markup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sedan | Toyota | $22,000 | $25,000 | $3,000 |
| SUV | Ford | $30,000 | $35,000 | $5,000 |
| Truck | Chevrolet | $40,000 | $48,000 | $8,000 |
| Electric Vehicle | Tesla | $45,000 | $55,000 | $10,000 |
Dealer Incentives and Holdbacks
Dealerships often receive incentives from manufacturers to sell certain models or meet sales targets. These incentives reduce the dealer’s cost, indirectly affecting the invoice price. Dealer holdbacks are a percentage of the MSRP that the manufacturer retains and pays to the dealer later, typically after the vehicle is sold. This functions as a hidden profit for the dealership, further influencing their negotiation position.
Different types of dealer incentives include volume bonuses (for selling a certain number of vehicles), conquest bonuses (for selling to customers who own competing brands), and seasonal incentives (to boost sales during slow periods).
The following flowchart illustrates the calculation of the final price:
Start → Invoice Price → Add Dealer Incentives → Subtract Dealer Holdback → Add Dealer Markup → Add Additional Fees (destination, taxes, etc.) → Final Price
Negotiation and the Invoice Price, What is invoice price on a new car mean
Source: simpleinvoice17.net
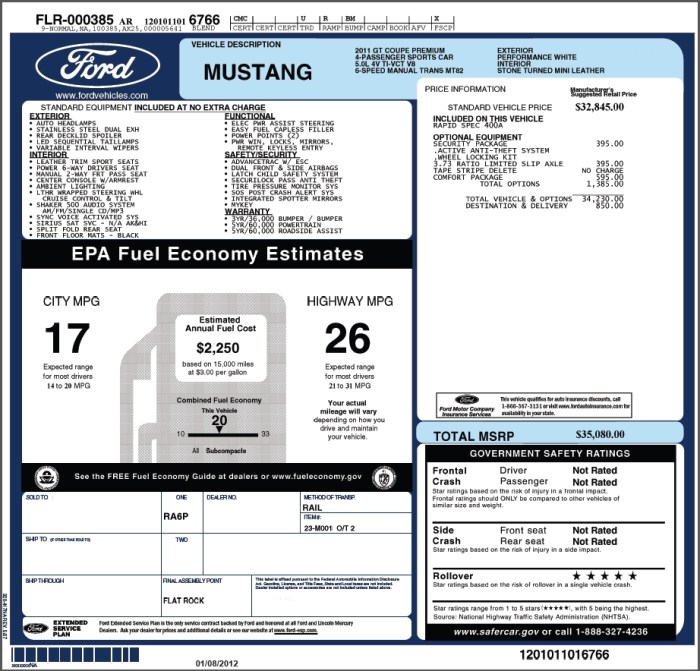
Using the invoice price as a starting point in negotiations provides a solid foundation for a fair deal. Dealerships often employ tactics such as focusing on the MSRP, highlighting additional packages or features, or creating a sense of urgency. Buyers can counter these tactics by remaining calm, doing thorough research, and highlighting the invoice price as the baseline for negotiation.
A step-by-step guide for negotiating a car price based on the invoice price includes researching the invoice price, preparing a budget, visiting multiple dealerships, and not being afraid to walk away if a deal isn’t favorable.
Additional Fees and Charges
Beyond the invoice price, several additional fees inflate the final cost. These include destination charges (shipping costs), government fees (taxes, registration), and dealer preparation fees (for detailing and inspections). These fees vary across manufacturers and regions. Buyers should be aware of potential hidden fees such as extended warranties, paint protection, and fabric protection.
- Destination Charges
- Taxes and Registration Fees
- Dealer Preparation Fees
- Extended Warranties
- Add-on Products (e.g., paint protection)
Understanding Financing and Invoice Price
Financing options significantly impact the overall cost of a vehicle. Interest rates and loan terms determine the monthly payments and the total amount paid over the loan’s life. A higher interest rate increases the total cost, while a longer loan term reduces monthly payments but increases the overall cost. A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, lowering both monthly payments and the total interest paid.
For example, a $30,000 loan at 5% interest over 60 months results in higher monthly payments than the same loan at 3% interest. A larger down payment reduces the loan principal, further impacting the monthly payment and overall cost.
Illustrative Example: A Hypothetical Car Purchase
Let’s consider a hypothetical purchase of a mid-size sedan. The MSRP is $28,000, the invoice price is $24,000, and the dealer negotiates a final sale price of $26,000. Additional fees include $1,000 for destination charges, $1,500 for taxes and fees, and $500 for dealer preparation. The total cost is $29,000. The buyer secures financing at 4% interest over 72 months with a $3,000 down payment.
Cost Breakdown:
Negotiated Price: $26,000
Destination Charges: $1,000
Taxes & Fees: $1,500
Dealer Prep: $500
Total: $29,000
This detailed breakdown shows how the final price is composed of the negotiated price and various additional fees.
Questions Often Asked
Can I always get a car at the invoice price?
While the invoice price is a helpful benchmark, securing a car at precisely this price is uncommon. Dealerships need to make a profit, so expect some markup, though ideally a significantly lower markup than the MSRP.
How do I find the invoice price of a specific car?
Several online resources provide invoice price estimates for new cars. These typically require entering the make, model, year, and desired trim level. Keep in mind that these are estimates and may not perfectly reflect the dealer’s actual cost.
What if the dealer refuses to disclose the invoice price?
While not legally obligated to reveal the invoice price, a dealer’s refusal might suggest they’re unwilling to negotiate fairly. This could be a signal to consider other dealerships.
Are there any legal protections regarding invoice price disclosure?
There aren’t specific laws mandating invoice price disclosure in most jurisdictions. However, deceptive advertising practices regarding pricing are generally illegal.




















